Motor & Sensor Production in a Pleasant Factory
Tamagawa Seiki, founded in 1938, has long run a thriving business as a maker of precision parts. The company got its start by manufacturing oil gauges for fighter planes, but now it develops and produces a wide range of precision parts including angle sensors, gyros, servomotors and step motors which are sold to makers of robots, machine tools, aircraft, military hardware and more. Since recently, Tamagawa Seiki’s resolvers (rotation angle detection sensors) have been used in power steering motors for hybrid vehicles (HVs) and electric vehicles (EVs).
Tamagawa Seiki entered the space business in the mid-1980s, starting with gyros used for the H-I rocket’s inertial navigation, followed by the development and manufacture of motors, encoders, resolvers and other equipment used in a variety of satellites and probes. The company’s products are also used in Kibo, the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) on the International Space Station (ISS), and Konotori, the space station supply ship.
Tamagawa Seiki manufactures its aeronautics-related products at the First Plant in Iida, Nagano Prefecture, adjacent to the company’s headquarters. The facility was constructed in 1942, when it was called the Iida Plant, and the original buildings still look the same, giving the site a unique charm. The Spacetronics Laboratory, which conducts research and development on astronautics products, is also located on the property.

Tamagawa Seiki’s First Plant in Iida, Nagano Prefecture. Some of the buildings still retain the same appearance they had when constructed in 1942.

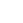
Since components for use in space are not mass produced, much of the production is done by hand. Precise work is essential for many of the processes involved. In the photo above, an employee is winding wires for motors and sensors.

Angle detector boards are assembled in a Class 1000 cleanroom. Precise records must be kept for every product manufactured and inspected in order to ensure reliability.



Tamagawa Seiki installed a space chamber to test and check products for use in space. Inside the chamber is a vacuum that simulates an outer space environment with a temperature range of -60 to +90 ℃ in order to check product durability.

The company installed a thermostatic chamber for testing and checking. This equipment can maintain a constant temperature with a variation of only +/-2℃ within a range of -70 to +120 ℃ in order to check product durability.

Most astronautics equipment is plated with gold to ensure conductivity and enhance durability. The photo above shows gold plating equipment installed in a cleanroom.

This line assembles motors. The photo shows a coil winding machine.
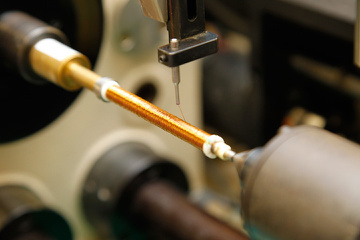

A motor assembly line also requires rigorous inspections. The photo shows an inspection operation for a linear motor.

This is a gyro assembly line. Gyros are produced in a Class 100000 cleanroom.

A history museum with displays of products resulting from Tamagawa Seiki’s R&D sits inside the First Plant.
TAMAGAWA SEIKI CO., LTD.
INTERVIEW
インタビュー
Enhancing Product Lineups
and Supplying Diverse Equipment
TAMAGAWA SEIKI CO., LTD.
Managing Director and First Plant Manager
Hideo Kumagai