Producing high-precision products through a processof processing and measurementscarried out repeatedly
The Hotaka plant of Harmonic Drive Systems is situated in the middle of a rural landscape in Azumino City, Nagano Prefecture. The company relocated to this site in 1990 after the Matsumoto plant that it established upon the founding of the company in 1970 (in Toyoshina, Azumino City) became too small from the expansion of its consumer lines of operations. The company produces Harmonic Drive® units according to a variety of specifications at a rate of 40,000 a month.
The Hotaka plant is the only production site operated by the company in the country. While group companies produce goods overseas in the United States and Germany, they produce a mere 4,000 units and 3,000 units, respectively, per month. The Hotaka plant can be described as the largest supplier of harmonic drive gearing units for consumer use in the world today.
Products for space applications began to ship in 1983. Since a high reduction gear ratio is obtained in the first stage, harmonic drive gearing units are suited for space equipment where weight reduction is essential. Harmonic drive gearing units are used in a wide range of different applications in the field of space, such as the rotary shaft drive for directing solar battery paddles towards the sun, drive shafts for directing high-gain antennas towards the earth, and articulated drive mechanisms built into space robots. They are also featured in the axle drive mechanisms of exploration rovers sent to other celestial bodies.
Products for space applications and products for consumer applications are both manufactured on the same line at the Hotaka plant. While 40,000 units are produced monthly, a majority of these units are built by hand. Once processing is completed, size measurements are taken. The unit is then subject to more processing. A skilled engineer repeats this process to finish the product in compliance with a high degree of precision.

Harmonic Drive Systems’ Hotaka plant where 40,000 Harmonic Drive® units are manufactured each month.

Raw materials are subject to an acceptance inspection.

The dimensions of a circular spline processed with a lathe are inspected (left). The required degree of precision is obtained by repeating this process of inspection and processing over and over again. The holes on a flex spline are being checked for size in the illustration shown on the right.

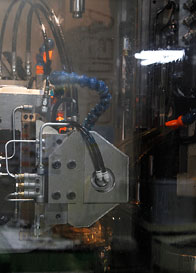
Using a gear-hobbing machine (left), the external teeth of a flex spline (right) are formed.


An elliptical wave generator into which bent bearings have been inserted is measured (left). The right illustration shows the manufacturing line for flex splines.


The assembly process. Rather than an assembly-line system, a yatai (food stalls) system characterized by the performance of all assembly steps for each unit by each worker has been adopted.


Final inspection process. Measurements (left) and performance (right) are stringently checked.


Completed Harmonic Drive® units (left). The company is also developing, in collaboration with Professor Masatoshi Ishikawa of Tokyo University, a robot hand featuring the world’s smallest Harmonic Drive® unit (with a 13-millimeter external profile) (right).
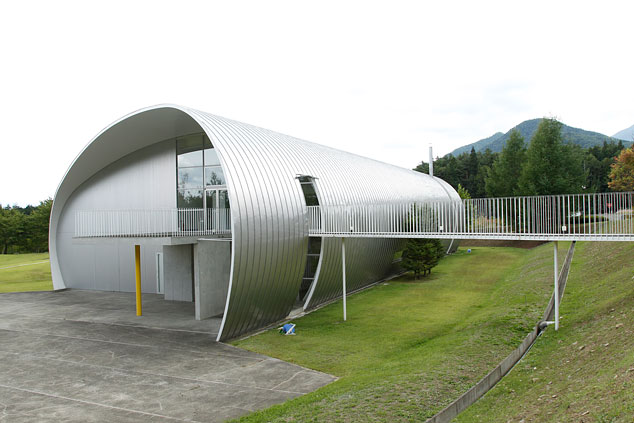


A uniquely shaped research laboratory. Research is normally conducted day and night without interruption in an environment maintained within half a degree above or below 23 degrees Celsius in hopes of improving precision by an order of magnitude.
HARMONIC DRIVE SYSTEMS
INTERVIEW
インタビュー
We also make reduction gears for space by hand
on a regular production line
HARMONIC DRIVE SYSTEMS
Executive Officer, Member of the Board
Yoshihide Kiyosawa