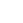
Turbopump seals undergo final inspectionsin a clean room.
Eagle Industry is a manufacturer that focuses primarily on mechanical—in other words, metal—seals. Compared to rubber seals, mechanical seals are characterized by the ability to tolerate harsh temperature environments (in terms of very high and very low temperatures). A manufacturer of rubber-based oil seals, Nippon Oil Seal Industry Co., Ltd., (currently known as “NOK”, also a manufacturer of flexible circuits) began developing mechanical seals in 1956. In 1964, Nippon Sealol was established through a merger with the American seal manufacturer Sealol. The mechanical seal division of this company was spun off and became the corporate predecessor of Eagle Industry. This company changed its name into what it is known as today in 1978 and subsequently severed capital ties with the United States. It is now a corporate member of the NOK Group.
The biggest clients of this company can be found in the automotive industry. The company supplies mechanical seals, bellows, valves, and other parts for engines, vehicular air-conditioning systems, and elsewhere and accounts for 65 percent of the global market for water pump seals, 70 percent of the global market for control valves, and 90 percent of the global market for lip seals. The company occupies an indispensable position in different industries in terms of its role in supplying gas seals for large compressors and mechanical seals for process pumps in the petrochemical industry, seals used in gas and steam turbines for electric generators in the energy industry, vacuum seals for the semiconductor industry, and screw-shaft seals for ships. Eagle Industry accounts for 70 percent of the total domestic market for mechanical seals.
At the same time, brush seals used in jet engines and other seals used with terrestrial gas turbines account for nearly half of the sales earned by the Aerospace Business Unit. Even then, seals for jet engines are supplied for 100 percent of engines domestically produced for the Ministry of Defense. All turbopump seals for domestic rockets are produced by this company.
The Aerospace Business Unit is located at the company’s Saitama site in Sakado City, Saitama Prefecture. With the exception of bellows and certain other products, everything from the development of technologies to the design and product manufacturing steps is carried out at this site. Out of 242 total employees at the company’s Saitama site, 114 are employees in the Aerospace Business Unit. In addition, sales teams affiliated with the Aerospace Business Unit and consisting of several employees each are permanently stationed in Tokyo, Nagoya, and Kobe.
Space parts are built through the heavy use of general-purpose machine tools. Since the quantities manufactured are low, however, the same item is never produced on the same machine for very long. Instead, the items manufactured are changed frequently. Another significant feature is the implementation of an exceedingly strict quality control system, part of which involves inspections of all items manufactured. In particular, for the turbopump seals in rocket engines where dust avoidance is an issue of paramount concern, cleaning, final inspections, and retention are carried out in a dedicated clean room.
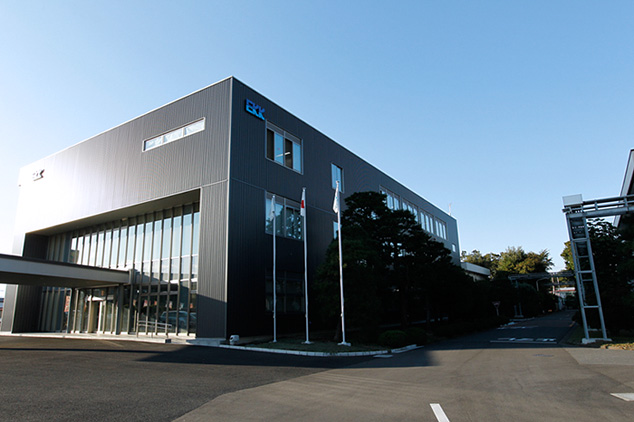

Eagle Industry’s Saitama site is in Sakado City, Saitama Prefecture. This is where products for the aerospace field are produced.

Since the manufactured quantity of any given space part is low, manufacturing is carried out with general-purpose machine tools. A grinding machine is shown on the left while a lathe appears on the right.


Brush seals and other mechanical seals with complex forms are made with a wire electric discharge machine (machine in the back). A processed part is being inspected in the forefront of this photograph.

Seal cases made from a nickel-based alloy or titanium alloy are fortified by being heat treated in a vacuum furnace.

A precision measurement room. Using a three-dimensional measuring machine or image-measuring machine, the dimensions of a completed part are measured with a high degree of precision. The same temperature and humidity levels are maintained year-round.

High-speed rotary testing equipment. Actual machine conditions are simulated in verification tests and durability tests on mechanical seals. Seals can be rotated at up to 50,000 rotations per minute (rpm) in a high-temperature environment of up to 400 degrees Celsius.

Turbopump seals for rocket engines are inspected in a class 100,000 clean room. This photograph depicts a load test.

For space parts that need to be welded, even the tiniest amount of dust is not permitted to adhere to the welded spot. For this reason, welding takes place inside a clean room. This welding machine was developed by the company.

Completed turbopump seals are stored on a class 100 clean bench.

Robots are also used to manufacture mass-produced seals for aircraft engines.

Analytical equipment consisting of a SEM (scanning electron microscope, left) and EPMA (electron probe microanalyzer, right) are also employed for the research on seal materials.


The design room of the Aerospace Business Unit’s Engineering Department. The Saitama site is home to 114 employees of the Aerospace Business Unit. These employees are engaged in design, manufacturing, quality assurance, and other work.

Key members of the Aerospace Business Unit. From left to right: Hiroshi Matsumoto, deputy head of the Business Unit; Tetsuya Iguchi, head of the Engineering Department; Masayuki Nakajima, head of the Manufacturing Department; and Masaya Murakami, head of the Aerospace Quality Assurance Department
EAGLE INDUSTRY
INTERVIEW
インタビュー
We supply the mechanical seals used inJapanese liquid rocket engines.
EAGLE INDUSTRY
Head of the Engineering Department of the Aerospace Business Unit
Tetsuya Lguchi